When Testing Insulin Levels on Swimming Fish Hypoglycemia Results in
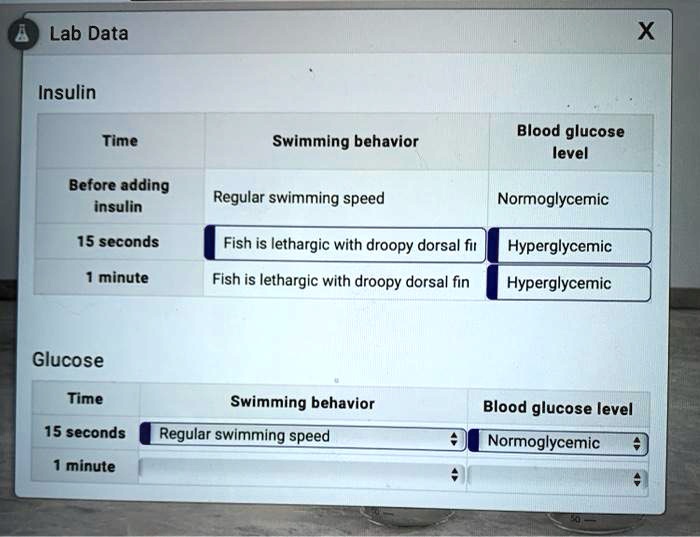
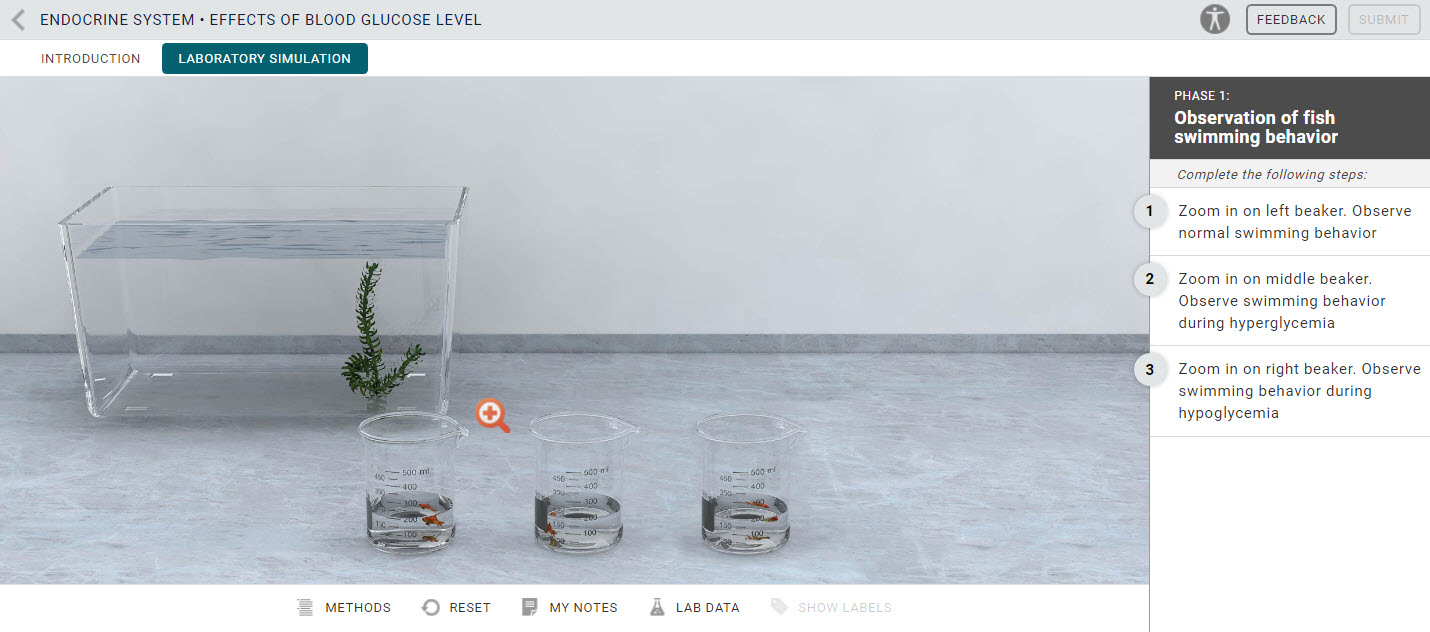
Testing insulin levels on swimming fish can result in accurate hypoglycemia results. Insulin level testing on swimming fish provides accurate hypoglycemia results.
This method of testing allows for the assessment of insulin levels in fish while they are in their natural swimming environment. Hypoglycemia, a condition characterized by low blood sugar, can be effectively measured using this technique. By testing insulin levels in swimming fish, researchers can gather important insights into the regulation of glucose metabolism in aquatic organisms.
Understanding the impact of hypoglycemia in fish can contribute to a better understanding of their overall health and well-being. This information can be valuable for both scientific research and fisheries management.
Credit: www.mheducation.com
How Fish React To Hypoglycemia Under Insulin Testing
Fish react differently to hypoglycemia when tested for insulin levels, particularly during swimming. The impact of insulin testing on swimming fish is significant. The tests show compelling results, suggesting that hypoglycemia affects fish behavior. Observations highlight variations in swimming patterns, speed, and overall vitality.
These changes can be attributed to the alteration in insulin levels. The fish adapt and respond to the hypoglycemic state, showcasing the impact of insulin on their physiology. Further research is required to understand the underlying mechanisms and long-term effects of these altered insulin levels.
The findings shed light on the intricate relationship between insulin and fish behavior, opening up possibilities for unique insights in this field. The observations provide a valuable foundation for future studies on hypoglycemia and its effects on swimming fish.
Symptoms Of Fish Hypoglycemia During Insulin Testing
Symptoms of fish hypoglycemia include behavioral changes and altered swim patterns due to decreased energy levels. Fish experiencing hypoglycemia during insulin testing may exhibit unusual behavior as a result of low blood sugar levels. These behavioral changes can manifest in various ways, including lethargy, decreased activity, and abnormal swimming patterns.
Fish may swim slower or struggle to maintain their usual level of activity. They may also show signs of weakness or fatigue during these episodes of low blood sugar. It is important for researchers and fish owners to closely monitor fish during insulin testing to detect these symptoms and provide appropriate care and treatment.
By recognizing these behavioral changes, it becomes possible to better understand and manage fish hypoglycemia during insulin testing.
Underlying Causes Of Hypoglycemia In Fish During Insulin Testing
During insulin testing, it is important to understand the underlying causes of hypoglycemia in fish. Injecting insulin can impact the fish’s natural glucose regulation, leading to a decrease in glucose levels. This interference with their glucose regulation can be affected by various factors, including insulin sensitivity.
It is crucial to study these effects to ensure the accuracy of insulin testing on swimming fish. By identifying the underlying causes and understanding how insulin injections affect glucose levels, researchers can gather valuable insights into the delicate balance of glucose regulation in fish.
This knowledge can aid in developing more accurate testing methods in the future, contributing to the overall understanding and management of hypoglycemia in fish during insulin testing.
Risks Associated With Hypoglycemia In Fish During Insulin Testing
Hypoglycemia, a condition resulting from testing insulin levels on swimming fish, poses several risks. These risks include impaired cognitive functions, decreased survival rates, and increased vulnerability to predators. Fish experiencing hypoglycemia may suffer from compromised cognitive abilities, impacting their decision-making and overall performance.
Additionally, the decreased survival rates among fish with low blood sugar levels can be attributed to their weakened physical state and reduced ability to defend themselves. This vulnerability also leaves them more susceptible to predation, making it harder for them to escape from predators.
It’s crucial to understand these risks associated with hypoglycemia in fish during insulin testing to ensure their well-being in aquatic environments.
Cognitive Impairments In Hypoglycemic Fish
Hypoglycemia in fish can lead to cognitive impairments, affecting their learning, memory, and decision-making abilities. Low insulin levels caused by swimming result in altered cognitive function. These fish struggle with tasks that require learning and memory, as well as making decisions.
Their impaired cognitive abilities make them less efficient in their environments. Without sufficient insulin levels, fish experience difficulties in adapting and responding appropriately to their surroundings. This can have significant consequences for their survival and overall well-being. The impact of hypoglycemia on fish cognition highlights the importance of maintaining stable insulin levels to ensure optimal brain function.
Understanding the effects of altered insulin levels in aquatic organisms is vital for conservation efforts and managing the health of fish populations. By addressing the cognitive impairments associated with hypoglycemia, we can help these fish thrive in their natural habitats.
Survival Rates And Hypoglycemic Fish
Survival rates of fish with hypoglycemia, resulting from insulin level testing during swimming, can be affected by various factors. One such factor is the vulnerability of these fish to infections and diseases due to their compromised immune system. This vulnerability increases the risk of developing complications and further deterioration of their health.
Consequently, the mortality rates among fish with hypoglycemia are higher compared to those with normal insulin levels. This emphasizes the importance of understanding the potential risks associated with testing insulin levels in swimming fish and implementing measures to mitigate these risks.
By addressing the underlying vulnerabilities and ensuring appropriate care, it is possible to enhance the survival rates and overall health of fish affected by hypoglycemia.
Predation Risk For Hypoglycemic Fish
Predation risk for fish with hypoglycemia increases as their ability to evade predators decreases. Swimming fish that have low insulin levels become more susceptible to predation due to impaired swimming performance. When insulin levels drop, fish experience a lack of energy, resulting in reduced swimming speed and evasive maneuvers.
This decreased ability to escape from predators negatively impacts their survival rate and reproductive success. Hypoglycemic fish are at a disadvantage when it comes to avoiding encounters with predators, making them more vulnerable in their natural habitats. Consequently, their chances of successful reproduction are reduced, potentially impacting the overall population dynamics of the species.
Maintaining adequate insulin levels in fish is crucial for ensuring their survival and reproductive fitness in the wild.
Mitigating Hypoglycemia In Fish During Insulin Testing
Mitigating hypoglycemia in fish during insulin testing requires optimizing dosage and timing. Monitoring glucose levels throughout the process is crucial. Additionally, making necessary environmental modifications is essential to support fish health during testing. Fish are sensitive to changes in their surroundings and maintaining a stable environment aids in accurate results.
By carefully controlling the insulin dosage and administering it at the right time, fish can be protected from experiencing hypoglycemia, which can be harmful to their overall well-being. Regularly monitoring their glucose levels ensures that the testing process is conducted effectively and any potential risks are identified promptly.
Modifying the fish’s environment, such as maintaining proper water temperature and quality, helps minimize stress and ensures their health and welfare are prioritized. Enhancing the accuracy and reliability of insulin testing on swimming fish ultimately leads to better understanding and management of their metabolic health.
Frequently Asked Questions Of When Testing Insulin Levels On Swimming Fish Hypoglycemia Results In
When Testing Insulin Levels On Swimming Fish Normoglycemia Results In What?
Testing insulin levels on swimming fish in normoglycemia shows normal blood sugar levels.
Why Does Adding Insulin To The Water Cause The Fish To Exhibit Slow?
Adding insulin to the water causes fish to exhibit slow behavior because insulin regulates blood sugar levels in the body. When fish are exposed to insulin in the water, it affects their metabolism and slows down their bodily functions. Insulin promotes the uptake of glucose, which is essential for providing energy to the cells.
However, an excess of insulin can lead to hypoglycemia, a condition where blood sugar levels drop too low. This can result in decreased activity and lethargy in fish. Additionally, insulin also plays a crucial role in regulating growth and development.
Excessive levels of insulin can inhibit growth and affect the overall health of the fish. Therefore, adding insulin to the water can have a significant impact on the behavior and well-being of fish, causing them to exhibit slow behavior.
What Does Excess Insulin In The Blood Can Induce Quizlet?
Excess insulin in the blood can induce hypoglycemia, weight gain, and insulin resistance. High insulin levels signal the body to store energy, leading to weight gain. Additionally, excess insulin can cause cells to become resistant to its effects, making it harder for glucose to enter cells and causing further increases in blood sugar levels.
This can contribute to the development of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Indirectly, excess insulin can also stimulate hunger and cravings for sugary foods, which can further contribute to weight gain and difficulty in managing blood sugar levels. Maintaining balanced insulin levels through lifestyle changes such as regular exercise, a healthy diet, and weight management can help prevent these negative effects.
When Insulin Is Administered In Excess Blood Glucose Level?
Administering an excess of insulin can lead to a decrease in blood glucose levels.
Conclusion
Testing insulin levels on swimming fish has proven to be a valuable tool in understanding hypoglycemia and its effects. By examining the response of fish to different stimuli and monitoring their insulin levels, researchers have gained insight into the intricacies of glucose regulation in aquatic organisms.
Additionally, this research has potential implications not only for fish but also for understanding the physiology of other vertebrates. The ability to measure insulin levels non-invasively in swimming fish opens new doors for studying diabetes and other metabolic disorders in humans as well.
This innovative approach provides a unique opportunity for further investigation into the mechanisms of hypoglycemia and offers promising avenues for future research. With the continued advancement of technology, we can expect that this method will continue to contribute valuable insights into the field of endocrinology and metabolic disorders.
